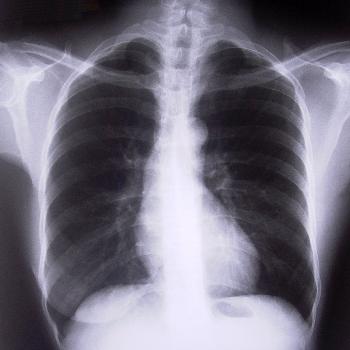
Purpose: The Chest X-Ray (One View) is designed to help healthcare providers diagnose and evaluate various conditions affecting the thoracic cavity, including:
- Pneumonia
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- Emphysema
- Heart failure
- Lung cancer
How It Works:
- The test uses a focused beam of radiation to penetrate the chest area, creating an image that depicts the chest's internal structures.
- In the resulting image, bones appear white, the heart appears as a lighter area, and the lungs appear darker, allowing for a clear differentiation between various tissues.
Procedure:
- During the X-ray, the patient stands facing the X-ray machine with their front toward it.
- The X-ray beam passes through the back of the chest first, minimizing the magnification of the heart and ensuring an accurate representation of the lungs.
- The X-ray captures the entire lung fields, ensuring minimal to no overlap of the scapulae borders on the lung fields for optimal clarity.
Analysis: After the imaging is complete, a radiologist will review the X-ray to identify any abnormalities or signs of disease, enabling timely diagnosis and treatment planning.
The Chest X-Ray (One View) is an essential diagnostic tool that provides crucial information about respiratory and cardiac health, facilitating prompt medical intervention when necessary.
Why would I need a Chest X-Ray (One View)?
A Chest X-Ray (One View) may be recommended if you:
Symptoms such as chest pain, persistent cough, shortness of breath, or fever may indicate a lung infection, heart problem, or other chest condition.
Monitor existing conditions, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), heart disease, or lung disease, to track any changes over time.
Had a recent injury: If you have had trauma to the chest area (e.g., from an accident or fall), an x-ray may help detect fractures or damage to organs within the chest.
Require a pre-employment or routine health screening, mainly if you work in environments where lung health is a concern or if you need to check for conditions like tuberculosis (TB).
Are undergoing follow-up care: An x-ray may be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatments, such as antibiotics for pneumonia, or after a procedure to verify recovery.