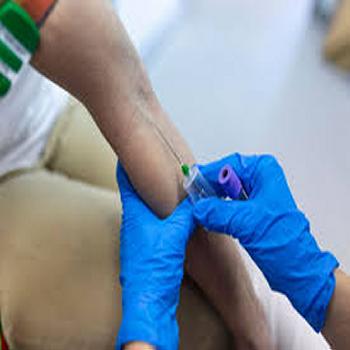
Why would I need a Blood Draw?
A blood draw is necessary for various reasons, including:
Routine health check-ups: Blood tests are often part of annual physicals or wellness exams to monitor overall health and detect abnormalities.
Diagnosis of medical conditions: Blood samples help diagnose various conditions, such as infections, anemia, diabetes, kidney or liver diseases, and hormonal imbalances.
Monitoring chronic conditions: Individuals with chronic conditions like diabetes, high cholesterol, or thyroid disorders require regular blood tests to track their health status and treatment effectiveness.
Pre-surgical evaluations: Blood tests are performed before surgeries to assess health parameters such as clotting factors and blood counts.
Screening for diseases: Blood samples are used for tests like cholesterol panels, blood glucose levels, and tests for infectious diseases (e.g., HIV and hepatitis).
How do I prepare for a Blood Draw?
Preparation for a blood draw may vary depending on the type of test, but general tips include:
Fasting: For specific tests, such as blood glucose or lipid panels, you may be asked to fast for 8–12 hours before the blood draw. Only water is usually allowed during this time.
Hydration: Drinking plenty of water before the procedure helps make veins more straightforward to locate and access, making the blood draw quicker and more comfortable.
Avoiding certain medications: Some medications or supplements can affect blood test results. Your healthcare provider will inform you if anything needs to be paused temporarily before the blood draw.
Wearing comfortable clothing: Short sleeves or clothing with sleeves that can be rolled up make it easier for the phlebotomist to access your arm.
Staying relaxed: Relaxing and taking deep breaths can help reduce anxiety or discomfort during the procedure.