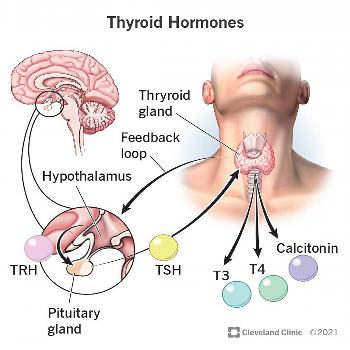
Purpose:
- TSH Test: Assesses thyroid gland function; high levels may indicate hypothyroidism, while low levels suggest hyperthyroidism.
- Total Testosterone Test: Measures overall testosterone levels; used to evaluate conditions like low testosterone (hypogonadism), infertility, or endocrine disorders.
Procedure:
- A blood sample is drawn from a vein, usually in the arm.
- The sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Interpretation:
- TSH Levels: Normal range typically between 0.4 and 4.0 mIU/L.
- Total Testosterone Levels: Normal ranges vary by age and sex (e.g., 300-1,000 ng/dL for adult males).
Preparation:
- Fasting may not be required, but it's best to follow any specific instructions from your healthcare provider.
- Inform your doctor about any medications, as they may affect test results.
Benefits:
- Aids in diagnosing thyroid disorders and hormonal imbalances.
- Helps guide treatment decisions for conditions related to thyroid and testosterone levels.
Safety: Minimal risks associated with blood draws, such as bruising or discomfort at the injection site.
Aftercare: No special care required; patients can resume normal activities immediately.
This dual test provides valuable insights into metabolic and reproductive health, facilitating effective diagnosis and treatment planning.
Why would I need a Total Testosterone Test?
A Total Testosterone Test may be recommended for:
Men experiencing symptoms such as reduced libido, erectile dysfunction, fatigue, decreased muscle mass, or infertility, which may indicate low testosterone levels (hypogonadism).
Women with symptoms of high testosterone levels, such as irregular periods, acne, excessive hair growth (hirsutism), or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
Evaluating puberty issues: The test can assess early or delayed puberty in children and adolescents.
Monitoring hormone therapy: If you are undergoing testosterone replacement therapy or treatment for other hormone-related conditions, the test helps monitor treatment effectiveness.
How do I prepare for a Total Testosterone Test?
Timing: Testosterone levels fluctuate throughout the day, typically peaking in the morning. For the most accurate results, the test is usually performed in the early morning, typically between 7 and 10 a.m.
Medications: Inform your healthcare provider about any medications or supplements you are taking, as certain medications (e.g., steroids, hormone therapy) can influence testosterone levels.
Fasting: Fasting is not required for a testosterone test, but your healthcare provider may give specific instructions based on your health status or other tests being conducted simultaneously.